When it comes to the health and wellness industry, CBD has become the new buzzword for those looking to cash in on the cash crop that hemp has grown after the 2018 Farm Bill relaxed industrial hemp production. Natural health nuts and practitioners of alternative forms of medicine swear by the substance and its alleged health benefits. But many are still reluctant to accept the possible benefits of a material derived from what most consider to be marijuana, let alone begin incorporating it into their daily routines.
What’s the reason for all this apprehension? Well, many are still worried about the legality of purchasing and taking cannabidiol in their state. State legislation is not always in line with federal rules, making it difficult to get a clear answer on this continuously grey area of the laws surrounding CBD.
Others worry about the makeup of CBD and the fact that it is derived from hemp, a plant that is sometimes conflated with marijuana and tied to specific social stigmas. Some even worry about side effects as well as the addictive properties of CBD, comparing it to the psychoactive properties that are associated with THC. In this article, we are going to address some of these concerns as well as break down the effects, benefits, and uses of CBD in comparison to THC products.
What is CBD? What is THC?
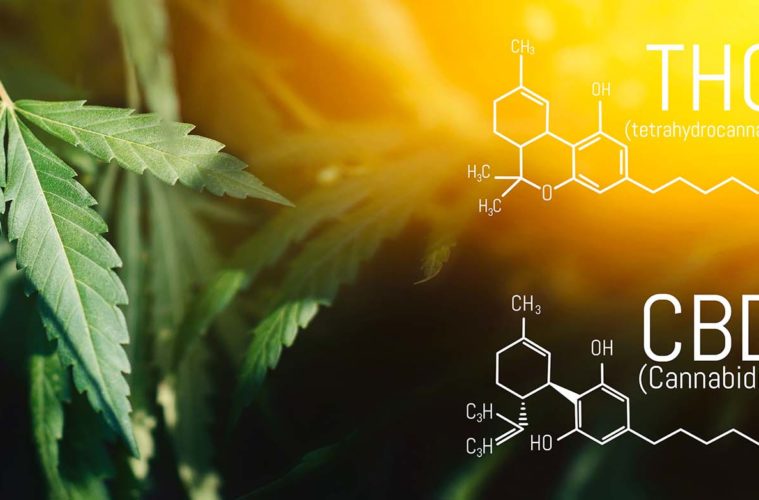
CBD, also known as cannabidiol, and THC, also known as tetrahydrocannabinol, are two occurring natural components found in cannabis plants. This genus describes both marijuana as well as industrial hemp. Cannabidiol can be extracted from both industrial hemp as well as marijuana; however, the majority of CBD made for purchase in the U.S. today is extracted from industrial hemp. This is because the federal ruling states that all hemp plants that are used for CBD extraction must meet the criteria of containing less than 0.3 percent THC in the entirety of the plant. Marijuana plants will contain higher concentrations of THC, making extraction and sale of CBD from these plants illegal in most states as well as illegal on a federal level.
THC is the component in marijuana that is responsible for the psychoactive effects usually associated with marijuana use, also known as a “high.” Although both CBD and THC share a similar molecular formula, CBD does not induce any sort of psychoactive effects on the user. This opens up the doorway for people seeking alternative health benefits associated with cannabis while avoiding unwanted psychoactive side effects.
Both THC and CBD interact with our body’s endocannabinoid system but have different effects on it. The endocannabinoid system in our body plays a role in helping us regulate different processes and functions in our bodies, including sleep, appetite, mood, memory, inflammation, muscle formation, and homeostasis. Whether or not we ingest CBD or THC does not change the fact that our body has its own complex system of cells called endocannabinoids that are naturally produced within it. Similar to cannabinoids, endocannabinoids help keep the internal functions inside you running smoothly. There are also endocannabinoid receptors that send signals throughout the body and are what CBD and THC bind to in order to release specific effects. CBD, in particular, is often used in order to aid pain management by binding to these receptors and blocking signals to the nervous system.
Flowers that contain both THC and CBD are often suggested for first-time marijuana smokers as CBD can also help block some of the psychoactive effects of THC by binding to the receptors and keep them from activating the “high” sensation as powerfully.
This is because THC binds to and stimulates CB1 receptors in the brain, causing the psychoactive effects of the THC. CBD, on the other hand, does not bind to CB1 receptors as strongly and can actually prevent the CB1 receptors from binding to other cannabinoids, keeping the effects of the THC at bay.
Where do CBD and THC come from?
Both CBD and THC are extracted from plants in the cannabis genus, which includes both hemp and marijuana. However, the extraction process for both compounds are very different. THC is most commonly extracted from the flowers, stalks, and leaves of the marijuana plant and then added to edibles, topicals, and other wellness products. Others may smoke dried cannabis flowers in order to feel the psychoactive effects of the compound.
CBD, on the other hand, is extracted in a few ways, including but not limited to chemical solvents as well as CO2 extraction. The CO2 extraction process uses pressurized carbon dioxide in order to filter out the plant’s terpenes, cannabinoids, and plant matter. CO2 extraction is also used as an extraction method for the food and herbal supplement industry. Cannabidiol that is processed through CO2 extraction is often considered premium-quality and can be used in tinctures or cartridges for vaping.
Legal Status of THC vs. CBD
On a federal level, THC is considered illegal, with some exceptions at the state level. Some states allow the use and sale of THC when it comes in the form of medical marijuana and for specific medicinal purposes. Recreational marijuana use is permitted in some states, but possession and use of THC in public spaces is still heavily regulated, especially in specific minority communities.
CBD, however, was given more freedom when the 2018 farm bill was passed, lifting the harsh restrictions that were once placed on hemp when it was conflated with THC-rich marijuana despite not containing any psychoactive components. That being said, some states still bar the use, sale, and import/export of CBD products from other states. It is also essential to keep in mind that if you sell CBD products under the guise of medicine and or dietary supplements, it is still considered illegal. Sale of foods that are infused with CBD are also regarded as illegal on a federal level. With that in mind, always make sure to find out the rules and regulations surrounding CBD in your state if you are looking to use CBD products.
Medical Benefits of CBD vs. THC
Although more scientific research needs to be done in order to gain conclusive information about the benefits of CBD, it is still considered to be a useful aid in helping with certain conditions as well as everyday aches, pains, and stressors. CBD is popularly used to help manage symptoms and conditions associated with epilepsy, aches and pains in joints and muscles, anxiety, stress, depression, Crohn’s disease, and opioid withdrawal. Early clinical research coupled together with anecdotal evidence suggests that CBD can be used to help manage a variety of symptoms and side effects of certain conditions without any of the psychoactive effects that are attributed to THC usage.
CBD is also considered to be non-addictive and can be ingested in large doses with little to no serious side effects. Clinical trials that have shown positive effects of CBD center around use in the aid of epileptic seizures, insomnia, as well as anxiety.
That being said, the long-term effects of CBD usage, tolerance levels, and clear criteria on dosage for CBD still need to be created in order to create a more structural guideline for people with a growing interest in CBD. This, of course, comes with time and will likely create a greater acceptance of CBD in both casual and medical settings.
THC is a component that is best known for the euphoric effects that it induces in consumers of the substance, but it also has certain medical benefits that can sometimes overlap with the benefits of CBD. It is often used to help relieve nausea symptoms, loss of appetite, and other symptoms that are common side effects of cancer treatment. Sometimes CBD and THC will be used conjunctively in order to relieve symptoms for patients in medical settings with high CBD strains of marijuana. These strains are also beneficial for those who are more sensitive to the side effects of THC, such as anxiety, paranoia, or dizziness.
Forms of CBD vs. THC
Some of the more common types of CBD are concentrated tinctures, capsules, edibles such as gummies, as well as topicals like bath bombs, balms, salves, and creams for muscle and joint pains. CBD can also come in cartridges for use in vaporizer products. Each method of cannabidiol consumption has its own benefits in the treatment of certain symptoms as well as for everyday wellness benefits.
Tinctures are taken sublingually and often attributed to the fastest absorption rate in the body and thus allows the consumer to feel the effects faster. Taking CBD in an edible will take longer to feel the results as it is slowly digested and absorbed into the body, but oftentimes the length of the effect will be longer. That being said, edibles are not as useful in particular settings, such as when one is experiencing anxious thoughts or onset panic.
Vaping CBD could be more useful in situations where one is put under duress and can give users a familiar sensation if they were also a prior cigarette smoker.
THC is also found in many forms, including but not limited to tinctures, shatter or dabs, infused-teas and drinks, edibles, and dried flowers.
Advertising disclosure: We may receive compensation for some of the links in our stories. Thank you for supporting Irvine Weekly and our advertisers.